Blog Editor’s Note: The recent action at ICAO’s Assembly declaring GNSS disruption an urgent issue has increased focus on the issue within the aviation community.
One note about the below – The author says that the best form of protection from spoofing is with included authentication signals such as those that will be offered by Galileo. Authenticated signals/codes won’t necessarily protect against meaconing, or the interception and rebroadcast of navigation signals. The rebroadcast would also include the authentication codes and could still deceive the receiver.
Some have suggested that meaconing is the technique the Russians use in their anti-drone efforts that also sometimes make ships at sea report they are at airports.
We should also mention that, while GPS and GNSS are great services and a lot can be done to improve security, it’s never possible to “ensure” security.

What is spoofing and how can you ensure GPS security?
by Maria Simsky, technical writer, Septentrio
As technological advances make GPS/GNSS devices more affordable, our lives are becoming increasingly dependent on precise positioning and timing. The aviation sector has been using precise positioning GNSS for decades to help guide airplanes in landing approaches especially during difficult weather conditions.
The American WAAS and the European EGNOS are SBAS reference networks which provide airplanes with corrections needed for high-accuracy positioning. Such safety-critical receivers as those onboard airplanes and in SBAS networks must be robust against jamming and spoofing, to ensure security in aviation positioning.
GNSS refers to constellations of satellites broadcasting signals from space that transmit positioning and timing information to GNSS receivers on Earth. The receivers then use this information to determine their location. These systems include the American GPS, European Galileo, Russian GLONASS, Chinese BeiDou, Japanese QZSS (Michibiki) and the Indian NAVIC system.
What is GPS/GNSS spoofing?
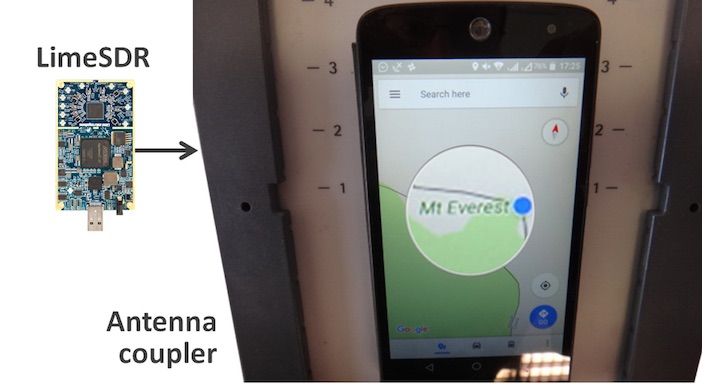
Radio interference can overpower weak GNSS signals, causing satellite signal loss and potentially loss of positioning. Spoofing, is an intelligent form of interference which makes the receiver believe it is at a false location. During a spoofing attack a radio transmitter located nearby sends fake GPS signals into the target receiver. For example, a cheap SDR (Software Defined Radio) can make a smartphone believe it’s on Mount Everest!
A cheap SDR (Software Defined Radio) can overpower GNSS signals and spoofs a single-frequency smartphone GPS into believing it is on Mount Everest
Why GPS spoofing?
Imagine a combat situation. Clearly, the side which uses GPS/GNSS technology would have an advantage over the side which does not. But what if one side could manipulate GPS receivers of their adversary? This could mean taking over control of autonomous vehicles and robotic devices which rely on GPS positioning. For example, in October 2018, Russia accused the US of spoofing a drone and redirecting it to attack a Russian air base in Syria.
In the last 3 years over 600 incidents of spoofing have been recorded in the seas near the Russian border. These ships appeared to be “transported” to nearby airports. This type of spoofing might have been introduced as a defense mechanism to ground spy drones. Most semi-professional drones on the market have a built-in geo-fencing mechanism which lands them automatically if they come close to airports or other restricted areas.
Some of the most enthusiastic spoofers are Pokémon GO fans who use cheap SDRs (Software Defined Radios) to spoof their GPS position and catch elusive pokémon without having to leave their room.
Types of Spoofing
Spoofers overpower relatively weak GNSS signals with radio signals carrying false positioning information. There are two ways of spoofing:
- Rebroadcasting GNSS signals recorded at another place or time (so-called meaconing)
- Generating and transmitting modified satellite signals